This course provides a comprehensive introduction to computer graphics, focusing on fundamental concepts and techniques in Computer Animation and Physics Simulation. Topics include numerical integration, 3D character modeling, keyframe animation, skinning/rigging, inverse kinematics, rigid body dynamics, deformable body simulation, and fluid simulation.
Forward and Inverse Kinematics
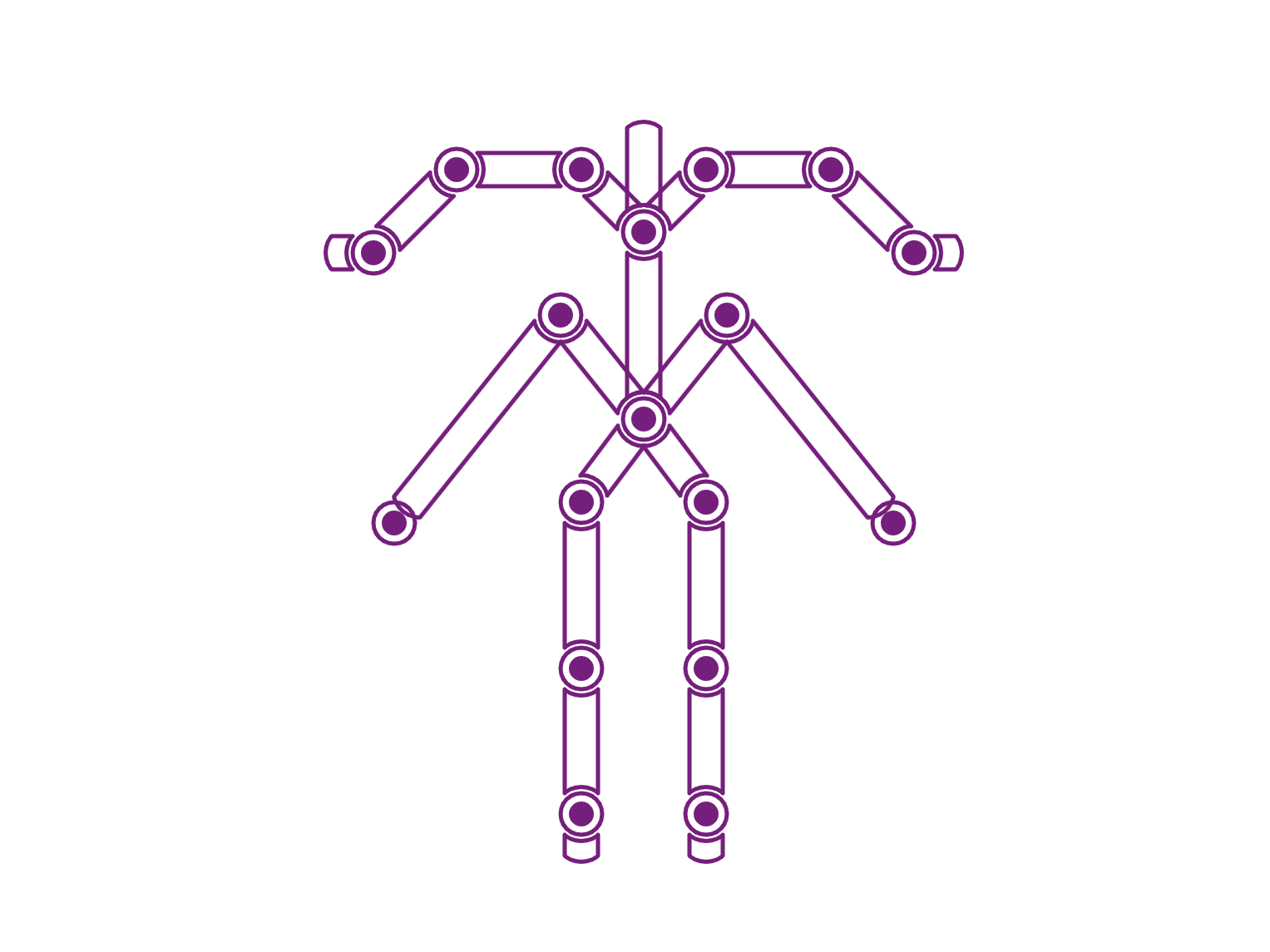
For Assignment One, we were tasked with constructing a joint hierarchy for a custom character to implement forward kinematics (FK) and inverse kinematics (IK). In FK mode, each joint, starting from the root, could be independently rotated or translated, with transformations propagating down the hierarchy to the child joints and bones, ensuring precise control over the character’s posture. Building on this, we implemented inverse kinematics (IK) using Jacobian matrices. This allowed the manipulation of end-effector positions, where adjustments at the lowest hierarchy elements translated through the chain, recalculating joint angles to achieve the desired global positioning while maintaining kinematic constraints.
Catmull-Rom & B-Spline Interpolation
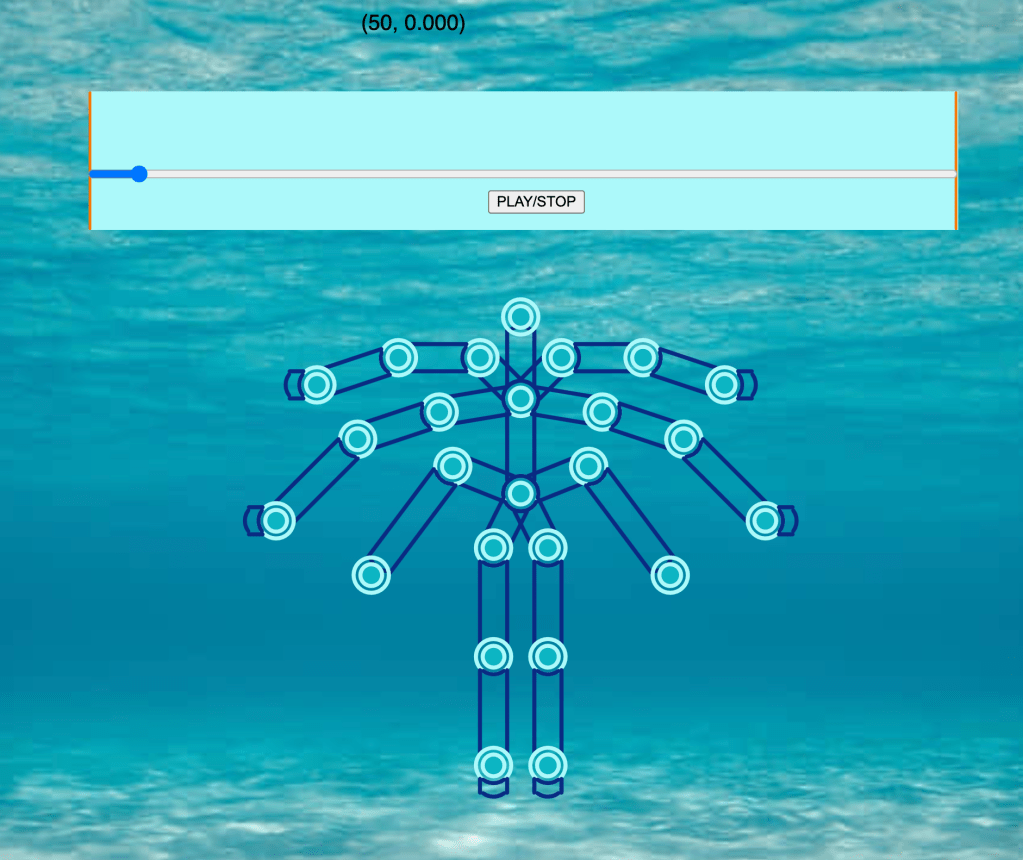
For Assignment 2, I built on my IK character to implement Catmull-Rom and B-Spline interpolation to create a key frame animation and compare the differences between animations based on their interpolation type. For Catmull-Rom interpolation, I used 4 keyframes to create smooth transitions between them. I calculate tangents at the keyframes to handle boundaries smoothly and use the Catmull-Rom basis functions for interpolation.
For B-spline interpolation, I also work with 4 keyframes, but this time I use blending functions that control how each keyframe affects the transition, making it more flexible and stable over longer sequences. Both methods loop through the keyframes and adjust based on the duration between them, with a fallback to linear interpolation if there are fewer than 4 keyframes.
This way, I ensure smooth, natural motion between keyframes while keeping the interpolation flexible for different scenarios.
Pinball, CCR & SDFs

For this pinball assignment, we were tasked with making an engaging and fun yet functioning machine. I created or modified all the elements in my machine, including creating Implementing a new Star SDF into the environment, adding a virtual plunger to launch the ball into play, and implementing points and lives count.
For Discrete Collision Resolution, I implemented the normal finite difference method (normalFD2(p)) to resolve collisions between objects in the game. This involved calculating the necessary response when objects collide, ensuring accurate interactions.
For Continuous Collision Resolution, I used ray marching to handle collisions in a way that accounts for continuous motion, providing more precise results than discrete methods. This allows for smoother and more realistic gameplay, especially when objects are moving fast.
Attack of the Minions!

In this assignment, I implemented various forces and collision handling to simulate blob deformation and interactions. The blobs experience stretching forces modeled as springs, with carefully tuned stiffness to maintain stability while preventing excessive stretching. I implemented bending forces based on the angles between connected vertices to encourage a round shape, adjusting the stiffness to balance smoothness and numerical stability. Compression forces were also implemented to maintain the blob’s area during collisions, preventing deflation. For collision detection, I used penalty forces and contact impulses for blob-environment interactions and broad-phase collision detection with AABBs for blob-blob collisions. Additionally, I added expressive features, including minion-like faces with changing colors based on the blob’s area, turning them into purple minions when the area deviates too much from the rest shape. One key challenge involved tuning the bending forces with a non-zero rest angle based on the number of particles, which required adjusting angular correction forces to maintain the blob’s shape and stability.
